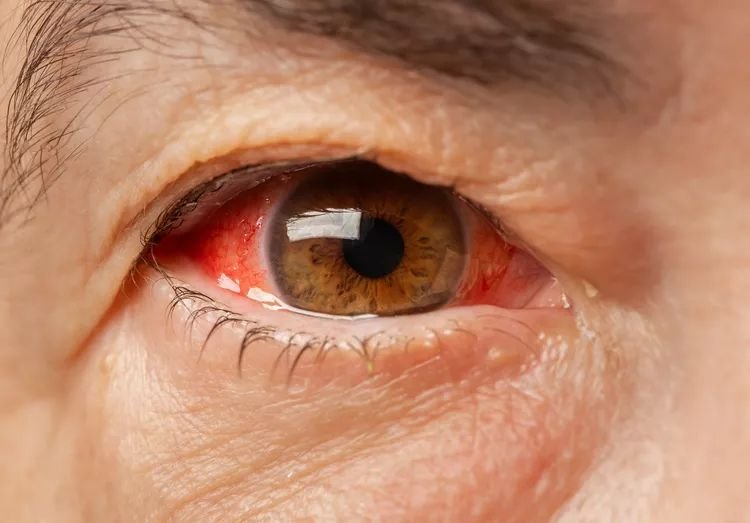
Introduction
Waking up with a red, painful eye can be alarming. Is it just a minor irritation, or could it be something more serious? Eye discomfort can range from mild to severe and may indicate various underlying conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the common causes of redness and pain in one eye, explore potential treatments, and highlight when it’s crucial to seek medical attention. Armed with this knowledge, you can take the necessary steps to protect your vision and eye health.
Conjunctivitis: The Common Culprit
One of the most frequent causes of redness and pain in one eye is conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye. This condition can be viral, bacterial, or allergic in origin, each with distinct symptoms and treatments.
Symptoms of Conjunctivitis
The eye appears red due to inflammation of the conjunctiva, the clear tissue covering the white part of the eye. Depending on the type, you may notice a watery (viral or allergic) or thick, yellow-green discharge (bacterial). Allergic conjunctivitis often comes with significant itching.
Treatment
Viral conjunctivitis typically resolves on its own within a week or two. Cold compresses and artificial tears can provide relief. Bacterial conjunctivitis requires antibiotic eye drops or ointments prescribed by a healthcare provider. Allergic conjunctivitis can be managed with over-the-counter antihistamine eye drops and by avoiding allergens.
Corneal Abrasion: A Painful Scratch
A corneal abrasion occurs when the surface of the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, gets scratched. This can happen due to foreign bodies like dust, sand, or even a fingernail.
Symptoms of Corneal Abrasion
The cornea is highly sensitive, making any scratch extremely painful. The eye becomes red as a response to the injury. The eye may water excessively and vision may be temporarily affected.
Treatment
Rinse the eye with clean water or saline solution to remove any debris. Avoid rubbing the eye, as this can worsen the abrasion. Seek medical attention; your doctor may prescribe antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection and recommend pain relievers.
Uveitis: Inflammation from Within
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, which can cause significant redness and pain. It can be associated with autoimmune disorders or infections.
Symptoms of Uveitis
Uveitis is characterized by intense pain, particularly around the eye, and is often associated with light sensitivity. Deep redness typically appears around the iris, and vision may be blurry, with floaters.
Treatment
Steroid eye drops are often used to reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, oral steroids or immunosuppressive drugs may be necessary. Treating any underlying autoimmune or infectious disease is crucial.
Glaucoma: The Silent Thief of Sight
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is a serious condition that can cause redness, pain, and vision loss. It occurs when the drainage angle of the eye becomes blocked, leading to a rapid increase in intraocular pressure.
Symptoms of Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma
Symptoms include severe eye pain, often accompanied by a headache. The eye may appear red and swollen. Nausea and vomiting can occur due to the intense pain, and vision may be blurred, with halos around lights.
Treatment
This condition requires immediate medical attention to prevent permanent vision loss. Doctors may use medications to lower eye pressure quickly. Procedures like laser therapy or surgical intervention may be necessary to create a new drainage pathway.
Dry Eye Syndrome: The Chronic Irritant
Dry eye syndrome occurs when your eyes don’t produce enough tears or the right quality of tears to keep the eye surface lubricated. It can cause redness and discomfort in one or both eyes.
Symptoms of Dry Eye Syndrome
Chronic irritation can lead to persistent redness. A gritty sensation, like there is something in your eye, may be present. Paradoxically, dry eyes can also cause excessive tearing as a reflex.
Treatment
Over-the-counter artificial tears can help lubricate the eyes. Reducing screen time, using a humidifier, and taking breaks can alleviate symptoms. In more severe cases, medications like cyclosporine (Restasis) or lifitegrast (Xiidra) may be prescribed.
Conclusion
Redness and pain in one eye can stem from various conditions, ranging from minor irritations to serious medical emergencies. Understanding the potential causes and appropriate treatments is essential for maintaining eye health and preventing complications. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate care. Your eyes are precious, and taking prompt action can help preserve your vision and overall well-being.
References
1. American Academy of Ophthalmology. (2021). Conjunctivitis: What Is Pink Eye?
2. Mayo Clinic. (2020). Corneal Abrasion (Scratched Eye).
3. National Eye Institute. (2022). Uveitis: Overview and Facts.
4. Glaucoma Research Foundation. (2021). Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Symptoms and Treatment.
5. Dry Eye Foundation. (2021). Understanding Dry Eye Disease.
